Solar Mounting Structures Market – India

With time, solar panels mounting systems technology has evolved in India. Power Insight takes a look into the various types of pv mounting structures prevalent in the market and key design precautions to keep in mind before installation of solar pv panel mounting system in a project.
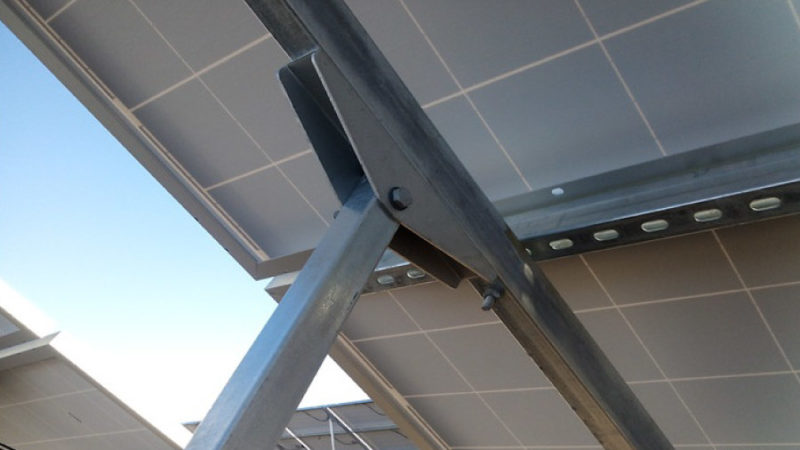
Solar mounting structures or “racking”, is at the foundation of every solar system. Having the right kind of racking can make or break an installation, as this determines the stability of the overall system.
With positive growth trends seen in the Indian solar power industry over the past two years investor confidence in the segment has increased over time. This has help in greater capacity additions and positive growth reflection across associated markets – such as mounting structures.
PV Mounting structures provide all the essential elements to drive solar power generation. They help tilt the panels at a specific angle thus ensuring maximum irradiation per unit area. Over the years, mounting structures have found applications beyond the traditional ground-mounted solar power plants. Today, mounting structures are increasingly
being used at rooftops, carports and other sites – irrespective of the surface.
Market Overview:
Two specific types of module mounting structures or systems are used in ground mount installations, that can be categorized by the tilt of the panels.
- Fixed Tilt Mounting Structure: The Fixed Tilt mounting structures are designed to provide the year-round optimum tilt to the solar panels. Here, the tilt of the modules cannot be changed once the structures and modules are installed. Thus these types of mounting structure are used in projects where the solar panels are typically facing the south direction.
- Seasonal Tilt Mounting Structure : While, on the other hand, the seasonal tilt structure allows the south-facing panels to be adjusted seasonally. In these mounting structures there are holes drilled into the bow of the base supporting structure that can be used to manually vary the tilt of the modules. The tilt of the modules can be varied from season to season, with changes in arc of the sun path across the sky. In most cases, the tilt of the modules is varied with the season changes of summer and winter.
- Tracker fitted Mounting Structures:These types of pv panels mounting systems are fitted with automated tracker technology to follow the sun movement through the day. Developers are also increasingly deploying solar tracker technology, where modules are mounted facing east-west and the tracker follows the sun’s path to maximize generation. This automates the manual process of physically changing the tilting the modules to the optimum angles.
Different types of module mounting structures may be used depending upon the design of the plant, and the cost constraints involved. These structures are composed of a mix of HDG and pre-galvanised steel, or galvalume. The majority of the projects are based on these technologies.
Designing Precautions
Module Mounting Structures play a critical role in setting up a durable, long-lasting and efficient solar power plant. With module design changing with rapid technological advancement along with increasing capacities of solar modules, weights and dimensions of the modules must also be examined carefully from design to design as they have a critical impact on the structural integrity of the installation.
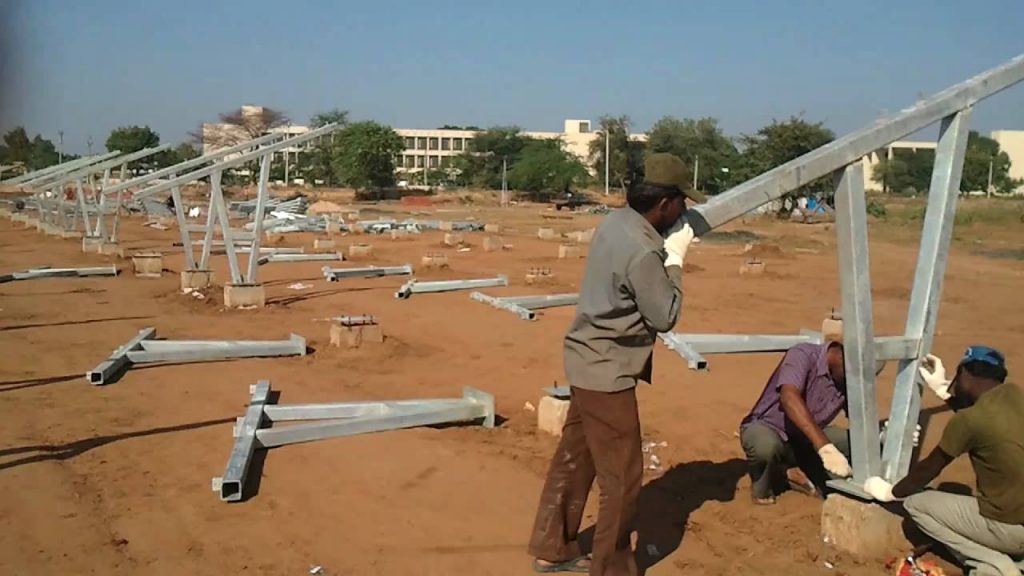

- Strong Foundation for Panels Mounting System:The first thing that should be examined before the setting up of module mounting structures, for a ground mount solar plant, is the foundation of these structures. A strong foundation is the key to a stable mounting structure. Further, in order to derive highly efficient designs, software tools may be employed, wherein local standards are used for reference. The most common inputs used are – Location (Latitude and Longitude) and Structure Tilt: This tilt is dependent on the location of installation.
- Material of Mounting Structure:The other important aspect to consider is the type of structural material. The material must allow for the structure to be sturdy so as to withstand the load of the module and the wind load. With these inputs, the optimized structure design and reactions for the foundation design are obtained.
Thus, the overall technical soundness of the plant can reach high levels of operation only when the Panels Mounting structures are designed and constructed with great care, and with close attention to detail. Partnering with the top solar companies in India is vital here!
Challenges
The competitive bidding process has certainly compelled developers to adopt cost-effective technology solutions. Keeping up with the market, the benchmark costs of pv panels mounting systems have also been decreasing in line with other capital costs.
Thus, the market has been flooded with mounting structure designs that are cost-competitive and easy to install in recent years. But these mounting structure are not strong enough to support the panels throughout the project life cycle. Further, customization of mounting structures as per the project requirements and site conditions, adds to the costs.
On the other hand, the cost of raw material such as steel and aluminium has also been fluctuating, affecting the mounting structures market. In addition, manufacturing issues and an influx of low-grade raw material from China are leading to quality issues across the industry. Certainly, the research and development in the raw material industry has not been able to sync with the rapid pace of developments in the solar power market.
Outlook
With increasing solar power installations in India, the market of mounting structures is expected to grow significantly in the near future. Steel-based structures are expected to dominate the market unless galvalume or other polymer-based materials become cost-competitive.
To produce mounting structures, 40-60 tonne of steel is required for 1 MW of solar power capacity. Over the next five years about 85 GW of solar power capacity has been planned. Thus, about 4.25 million tonnes of steel will be needed to realise the government’s solar target.According to various reports – the steel market for mounting structures could be worth Rs 25.5 billion over the next five years, if the country meets its 100 GW solar power target.
However, as steel prices are expected to increase due to high demand from the automotive sector. Also, the industry needs to invest in research and development to bring down the cost of mounting structures in line with the module prices and other capital costs.